Automate Unit tests using Github Actions
Setup unit tests in Github Actions
- tags
- #Github-Actions #Setup
- categories
- CI/CD
- published
- reading time
- 4 minutes
When we push changes to Github and raise a pull request, we want to make sure that we did not break our existing code and all our unit tests are passing. To ensure this, we can setup a workflow using Github Action to check if all our unit test cases in our app have passed or not.
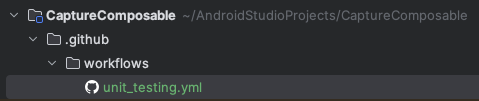
To create a workflow using Github Actions, create .github/workflow directory in the root directory of the app.
Create a unit_testing.yml file which will contain the workflow.
Workflow Setup
Let us first give our workflow a name
name: Unit Tests
Now, we want to define the trigger that will run our workflow. We want our workflow to run when a pull request is opened, reopened, or synchronized (new commits pushed).
name: Unit Tests
on:
pull_request:
types:
- opened
- synchronize
- reopened
Next, we define the job that will run this workflow. We define the name of the job and the runner that our job will be executed on. In our case, we will use ubuntu-latest as that is sufficient for our use case.
name: Unit Tests
on:
pull_request:
types:
- opened
- synchronize
- reopened
jobs:
unitTest:
name: Run unit tests
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
Now, we define all the steps required for our workflow. The first step, is to checkout our repository.
We can achieve this using the actions/checkout action. This will checkout the branch for which the pull request is raised.
name: Unit Tests
on:
pull_request:
types:
- opened
- synchronize
- reopened
jobs:
unitTest:
name: Run unit tests
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
The second step is to setup Java so that it can execute our code. You can use the Java version of your choice. We will be using temurin. It has several benefits like
- Has consistent and reliable releases
- Works consistently across different operating systems
- Widely adopted in CI/CD pipelines
- Good integration with GitHub Actions
name: Unit Tests
on:
pull_request:
types:
- opened
- synchronize
- reopened
jobs:
unitTest:
name: Run unit tests
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Set up JDK
uses: actions/setup-java@v4
with:
distribution: 'temurin'
java-version: '21'
The final setup is to actually execute our unit test cases. You can replace the gradle command with your platform specific command to execute the test cases.
name: Unit Tests
on:
pull_request:
types:
- opened
- synchronize
- reopened
jobs:
unitTest:
name: Run unit tests
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Set up JDK
uses: actions/setup-java@v4
with:
distribution: 'temurin'
java-version: '21'
- name: Unit tests
run: |
bash ./gradlew test
That is it. Push these changes to Github and the next time you raise a pull request, this workflow will run.
Common issues
Here are some of the most common issues for the action to not trigger after raising a pull request.
- Branch Protection Rules: Check if your branch protection rules prevent or block the action.
- Incorrect workflow directory: The workflow file not being in the correct directory.
/workflows/unit_testing.yml # ❌ Wrong /.github/workflow/unit_testing.yml # ❌ Wrong /.github/workflows/unit_testing.yml # ✅ Correct - Spelling mistakes in the event triggers:
on: pull-request: # ❌ Wrong (hyphen) pullrequest: # ❌ Wrong (no underscore) pull_request: # ✅ Correct - Permission Issues: Check if your repository has have Actions enabled.
- YAML syntax errors: Check for indentation. If the alignment in the workflow correctly, then the workflow might not run.
on pull_request: # ❌ Wrong indentation types: [opened] on: pull_request: # ✅ Correct indentation types: [opened]
Additional setup
You can also add additional steps like caching, runner timeout, writing test results to file and more in the workflow. Here is an example.
name: Unit Tests
on:
pull_request:
types:
- opened
- synchronize
jobs:
unitTest:
name: Run unit tests
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
timeout-minutes: 10 # Timeout to avoid the runner being in a dangle state forever
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Set up JDK
uses: actions/setup-java@v4
with:
distribution: 'temurin'
java-version: '21'
cache: 'gradle'
- name: Setup Gradle
uses: gradle/gradle-build-action@v2
# Caching
- name: Configure Gradle properties
run: |
mkdir -p ~/.gradle
echo "org.gradle.caching=true" >> ~/.gradle/gradle.properties
echo "org.gradle.parallel=true" >> ~/.gradle/gradle.properties
echo "org.gradle.daemon=false" >> ~/.gradle/gradle.properties
- name: Unit tests
run: |
./gradlew :composeApp:test --no-daemon
# This will write the test results (pass or fail) in a html file. Helpful in viewing failed test cases
- name: Upload Test Results
if: always()
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: test-results
path: composeApp/build/reports/tests/
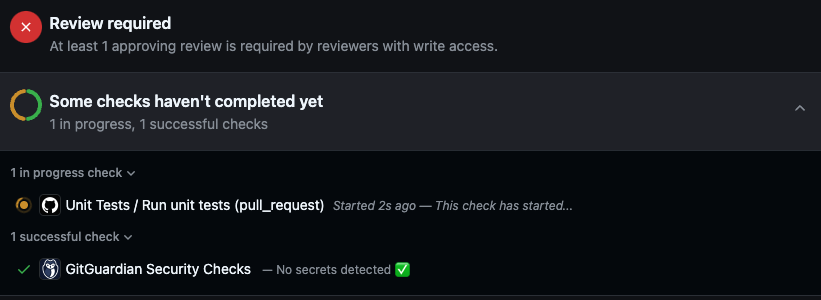
Example
Workflow running after raising a pull request
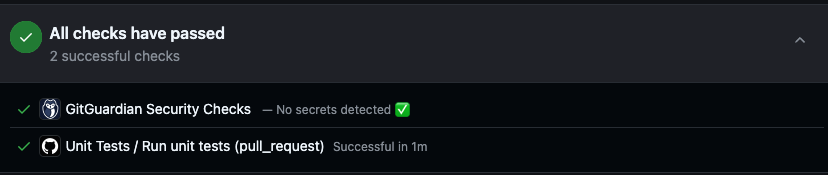
Workflow successful
You can refer this repository for reference. The workflow file is here.